In today’s world of ever-evolving cyber threats, building a vulnerability management program is essential for businesses to secure their networks and data. A vulnerability management plan helps organizations identify, prioritize, and remediate vulnerabilities in their IT infrastructure before cybercriminals exploit them. Let’s discuss the key components of a basic vulnerability management strategy and then we’ll provide a few implementation tips to help you get started.
Key Components of a Vulnerability Management Program
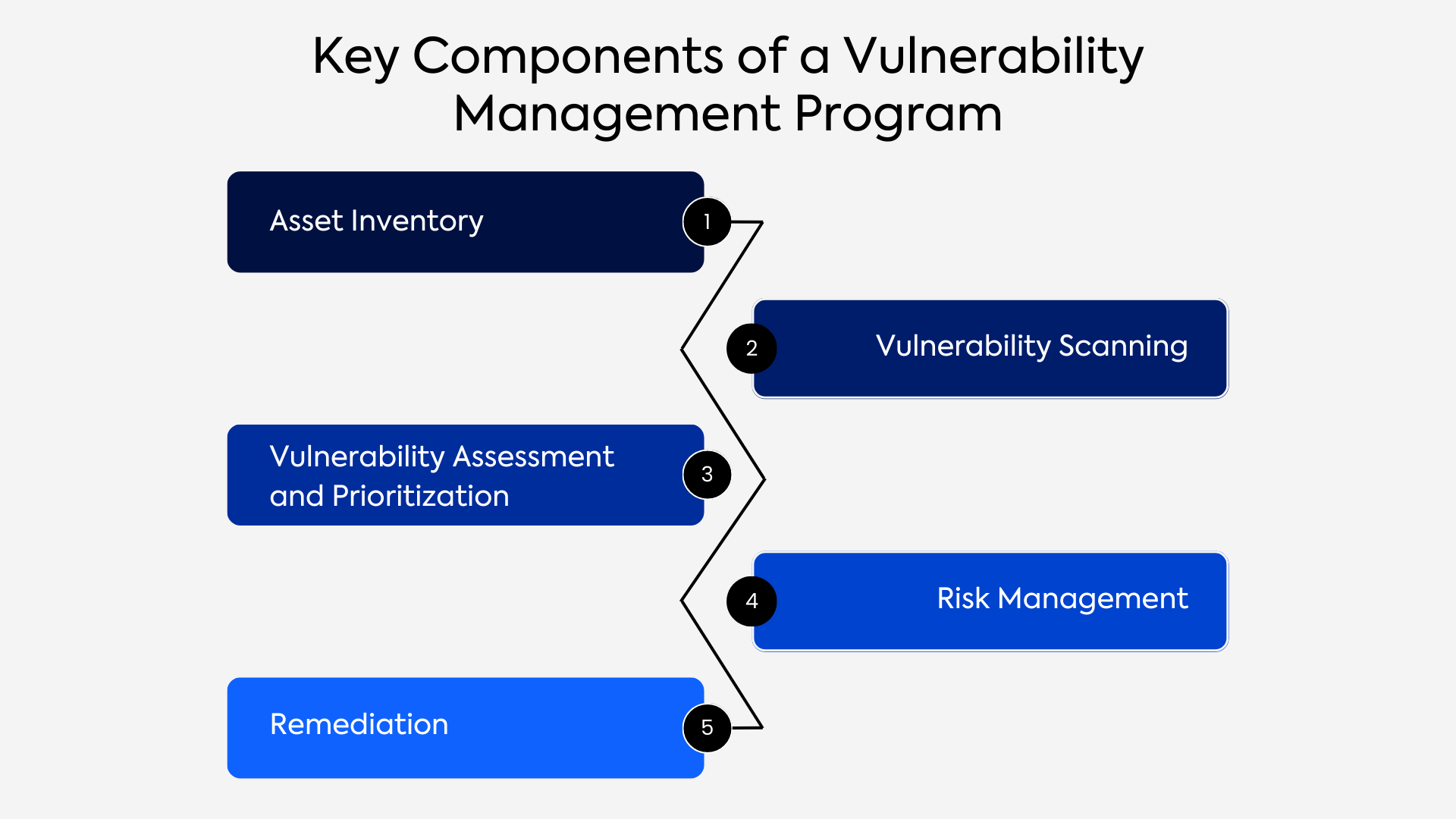
1. Asset Inventory:
The first step in building a vulnerability management plan is to create an inventory of all assets in your organization’s IT infrastructure. The asset inventory should include all hardware, software, applications, and devices that are connected to the network. This inventory will help you identify vulnerabilities and assess the risk associated with each asset.
2. Vulnerability Scanning:
Vulnerability scanning is the process of scanning the IT infrastructure for vulnerabilities. This process can be done using automated tools that scan the network for known vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability scanners identify vulnerabilities by looking for known software or configuration weaknesses in IT systems. The scanner can be configured to scan assets on a regular basis, providing continuous updates to the vulnerability status.
3. Vulnerability Assessment and Prioritization:
Vulnerability assessment involves analyzing the results of the vulnerability scan to identify vulnerabilities that pose a significant risk to your organization. Vulnerability assessment helps prioritize the vulnerabilities that need to be addressed first.
A vulnerability assessment should consider the potential impact of the vulnerability on the organization, the likelihood of the vulnerability being exploited, and the difficulty of exploiting the vulnerability and the type of asset that is at risk.
4. Risk Management:
Once vulnerabilities are identified and prioritized, the next step is to develop a risk management plan. The risk management plan should identify the actions that need to be taken to mitigate the risks associated with the vulnerabilities. The risk management plan should also include steps to monitor and review the effectiveness of the risk management plan.
5. Remediation:
Remediation involves fixing or patching vulnerabilities that have been identified. Remediation can be done using automated tools or manual processes. It is essential to prioritize remediation based on the severity of the vulnerability, the asset, and the potential impact on the organization. Once vulnerabilities have been remediated, you need to verify that the remediation is successful, and the vulnerability fixed.
In addition, a mature vulnerability management program reduces complexity by addressing the challenges of siloed teams, consolidating discrete network tools, and providing a unified view of tool and scan outputs, while removing the need to correlate separate spreadsheets and PDFs.
Implementation Tips for a Vulnerability Management Program
- Start with a Small Pilot Project: A vulnerability management program is a complex process, so it’s good to start small. A pilot project will help you identify the critical components of the vulnerability management plan and test the process.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders in the vulnerability management strategy, including IT teams, security teams, and business leaders. Stakeholders can provide valuable insights into the vulnerabilities that pose the most significant risks to the organization.
- Use Automated Tools: Vulnerability scanning, and remediation can be time-consuming processes. Use automated tools to streamline the process and reduce the time required to identify and remediate vulnerabilities.
- Regularly Review and Update the Program: Cyber threats are continually evolving, and it’s important to review and update the vulnerability management program regularly, ensuring the program remains effective and up to date.
- Provide Training: Provide training to all employees on the importance of the vulnerability management plan and how to report vulnerabilities. Training employees on how to identify and report vulnerabilities can help identify vulnerabilities that may have been missed.
Building a vulnerability management program is an essential step for organizations to secure their IT infrastructure and protect against cyber threats. A vulnerability management plan should include an asset inventory, vulnerability scanning, vulnerability assessment and prioritization, risk management, and remediation.
Implementing a vulnerability management strategy requires a strategic approach, starting with a pilot project, involving key stakeholders, using automated tools, regularly reviewing and updating the program, and training employees.
If you are interested in a robust vulnerability management program, Strobes VM365 checks all the above boxes and more. Our continuous vulnerability management plan combines manual processes with cutting edge automation, and brings tools, teams, and stakeholders together to fix critical issues fast. Gain visibility into risk based on assets, vulnerabilities, business units, and more while saving time and resources.
Conclusion:
A strong vulnerability management program is no longer optional, it’s a must-have for protecting your organization from increasingly aggressive threats. By following the key components outlined and applying the implementation tips, you can build a program that not only identifies and remediates vulnerabilities but also improves overall risk posture and operational efficiency.
If you’re ready to take the next step, start your free trail with Strobes to see how our platform can streamline your vulnerability management efforts and boost security across your organisation.
Related Reads:
- Difference in Traditional Vulnerability Management vs. Risk based Vulnerability Management
- The Role of Asset Correlation in Vulnerability Management
- Vulnerability Management Lifecycle: The Ultimate Guide to Business Security
- The Ultimate Guide to Vulnerability Assessment
- Vulnerability Management 10x faster
- Top 5 Vulnerability Management Mistakes Companies Make (Plus a Bonus Mistake to Avoid)
- What is Vulnerability Management? Compliance, Challenges, & Solutions
- Solution: Risk Based Vulnerability Management